Most Americans believe it’s normal for women to experience pain, pressure, and incontinence after childbirth, according to a new national survey by the Orlando Health Advanced Rehabilitation Institute. However, experts say these symptoms are actually signs of pelvic floor issues. While extremely common, affecting about a third of women, they are not normal (1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Definition & Facts for Bladder Control Problems (Urinary Incontinence)
).
Dispelling Myths About Pelvic Floor Health
“When we say it’s not normal, what we mean is it’s not something you should have to live with. It’s something you can rehabilitate and improve,” said Tessa Ladd, OTR/L, an occupational therapist at Orlando Health who specializes in treating pelvic floor dysfunction. “By strengthening and coordinating pelvic floor muscles and learning how to breathe and move in a way that supports the pelvic floor, these symptoms that so many women live with for years can be drastically improved.”
The survey, conducted by Ipsos, found that 71% of Americans agree it’s normal for women to have some urinary leakage after having kids, and more than half (51%) believe it’s normal for women to experience pain during sex after they’ve recovered from childbirth — both telltale signs of pelvic floor damage.
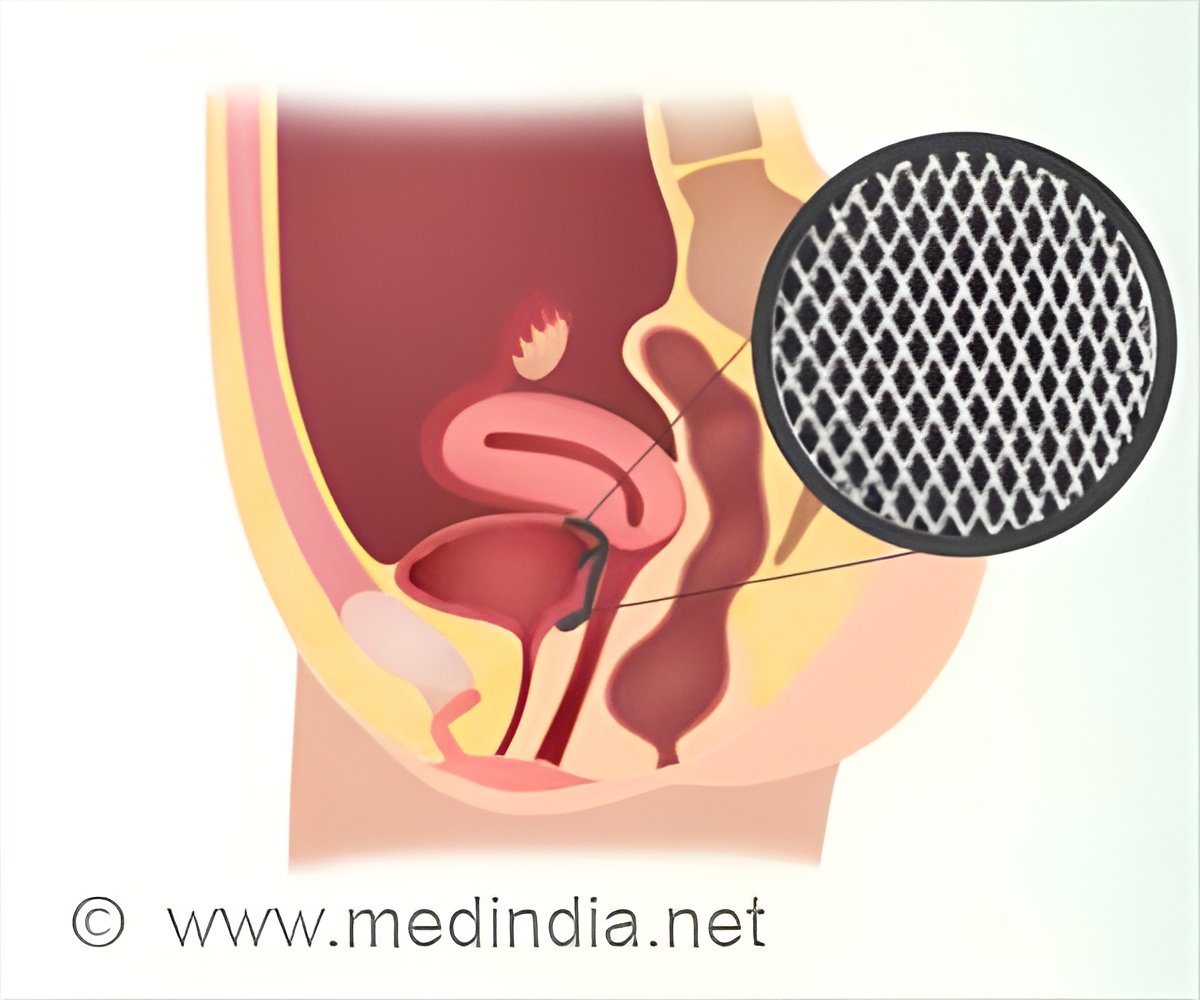
The pelvic floor is the group of muscles and ligaments that act as a “hammock” to support the vagina, uterus, bladder and rectum. When they become damaged — most commonly brought on by pregnancy, childbirth or aging — they can cause incontinence, as well as pain and pressure that occurs when these organs slip from their normal position, known as prolapse (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Is urine incontinence normal for women?
“Childbirth puts a lot of trauma on the body, but just like with any other injury, muscles and tissues should have the ability to recover and support the internal organs,” Ladd said. “If that doesn’t happen, we can step in and help. The muscles within the pelvic floor are skeletal muscles. They’re something that we do have control over, just like our biceps or our calves, and we have the ability to strengthen, lengthen and relax them.”
The Transformative Impact of Pelvic Floor Therapy
The survey also found that 71% of respondents believe women should start working out to strengthen their abs and pelvic floor as soon after childbirth as possible, something Ladd warns can be counterproductive, as women feel societal pressure to “bounce back” after having a baby.
“You can begin to do some deep breathing and learn correct body mechanics in that early postpartum phase, but it’s also important to allow your body time to heal and not to do too much too fast,” Ladd said.
Advertisement
About a month after having her second child, Nicole Gerardi-Lukens suddenly felt immense pressure in her pelvis and went to the hospital. After being diagnosed with bladder prolapse, she worried she’d need to undergo surgery and a lengthy recovery with a four-year-old and a newborn at home.
“I was so relieved when I was referred to a pelvic floor therapist,” Gerardi-Lukens said. “Tessa taught me things like how to breathe when I pick things up, and it made me realize how much pressure I was putting on my pelvic floor with everyday tasks. I didn’t always notice how much of that pressure I was feeling until I learned how to relieve it and could really feel the difference.”
Advertisement
After working with Ladd, Gerardi-Lukens can lift her child without the fear of pain or leakage, and says pelvic floor therapy is something she wishes she knew about sooner.
“You know your body, and you know when something’s not right,” Gerardi-Lukens said. “As moms, we so often put everyone else first and even laugh off things like leakage as just a part of motherhood, but you have to decide if these are things you want to deal with forever. And if they’re not, seek the help of a pelvic floor therapist.”
But before women can get the medical help they need, they have to acknowledge the problem. Talking to your health care provider is the first step to finding solutions.
“If we have a problem with our knee, we could talk to anyone about it without shame, without feeling uncomfortable or weird about it,” Ladd said. “Everyone has pelvic floor muscles, yet it’s something many women shy away from talking about, even with medical providers. When we open up about the symptoms we’re struggling with and understand that so many of us have this shared experience, we can help women live their lives free from pain and symptoms caused by these common and treatable issues.”
References:
- Definition & Facts for Bladder Control Problems (Urinary Incontinence) – (https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/bladder-control-problems/definition-facts)
- Is urine incontinence normal for women? – (https://www.mayoclinichealthsystem.org/hometown-health/speaking-of-health/is-urine-incontinence-normal-for-women)
Source-Eurekalert