Seaweed is a superfood packed with nutrients but comes with health considerations.

- Seaweed supports thyroid function due to its high iodine content
- Its fiber and bioactive compounds aid digestion and heart health
- Overconsumption can cause thyroid issues and heavy metal toxicity
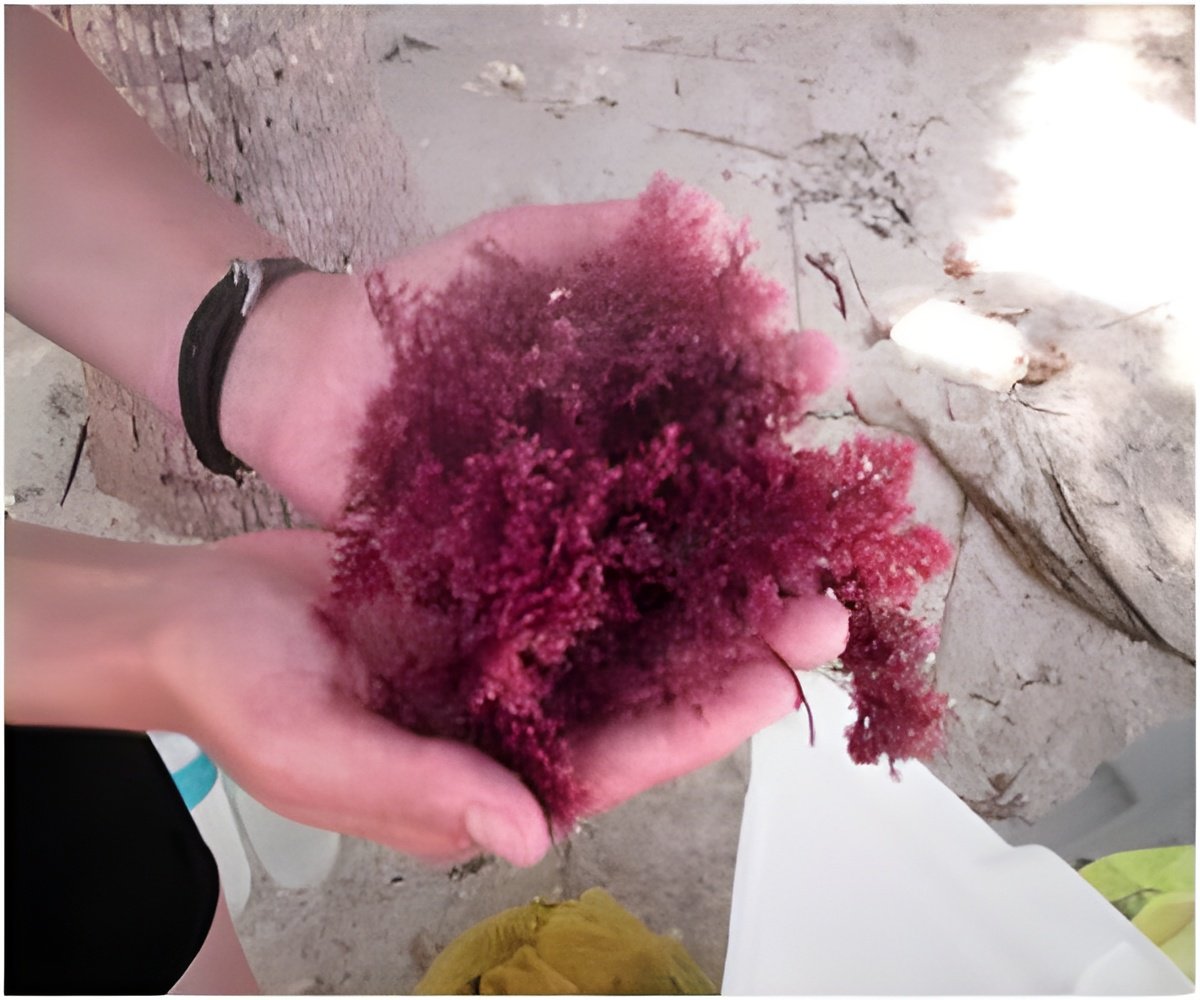
An ingredient that is an essential part of the diet across most Asian countries is seaweed. More than just a delicacy, it is a super-food. It is packed with vitamins, lots of minerals as well as antioxidants and has several potential health benefits. However, the chances of experiencing some ill effects is also present as consumption is increased above the recommended rate. This is what you should learn about seaweed’s advantages and disadvantages, how much of it you are recommended to consume, and possible negative outcomes (1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Impact of seaweed intake on health
).
How Much Seaweed Should You Eat?
This edible sea vegetable comes in various forms including but not limited to nori, kelp, wakame, kombu, and spirulina, thus it’s easy to integrate into the diet. A study conducted in Marine Drugs showed that seaweed comprises carbohydrates, proteins, minerals, dietary fibres, iodines, and polyunsaturated fats. It also contains bioactive compounds such as fucoidan and phlorotannins, offering numerous health benefits.
However, like all natural foods seaweed should be consumed in moderation because of the richness in nutrients. People are encouraged to take between 5-10 gm of dried seaweed per day according to nutritionists. The recommended intake varies depending on the type of seaweed:
- Instant Wakame: Up to 5 grams per day
- Kombu: About 5-6 centimeters per day
- Nori: Up to 15 grams per day
Potential Side Effects of Excessive Consumption of Seaweed
Excessive seaweed intake can lead to health problems due to its high iodine and heavy metal content:
- Hyperthyroidism: If taken more iodine than required, it leads to a hyperactive thyroid which is characterized by weight loss, increased heart rate, and nervousness among other symptoms.
- Iodine Toxicity: Though uncommon, it can still cause signs like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and some cases may lead to extreme conditions such as delirium and shock.
- Heavy Metal Exposure: Since seaweed is capable of harvesting nutrients and vitamins from water, most of them tend to include dangerous heavy metals like mercury and arsenic; therefore, if taken excessively it comes with dangerous effects to the health.
Seaweed is considered a ‘super food’ because it contains very essential nutrients that when taken in moderation, will help to boost your general health. Nonetheless, high consumption can lead to other severe health complications such as thyroid disorders and other heavy metal health complications.
This is augmented by the fact that one is supposed to adhere to portion control and speak to a doctor if they have any health complications or ways that they would like to change their diet.
The ocean’s gift of seaweed can boost your health—just remember, balance is the key.
Reference:
- Impact of seaweed intake on health – (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32908248/)
Source-Medindia