- Babesiosis is caused by the Babesia microti parasite transmitted through black-legged tick bites
- Symptoms range from mild to life-threatening, particularly for high-risk individuals
- Treatment includes antibiotics and anti-parasitic drugs, with hospitalization for severe cases
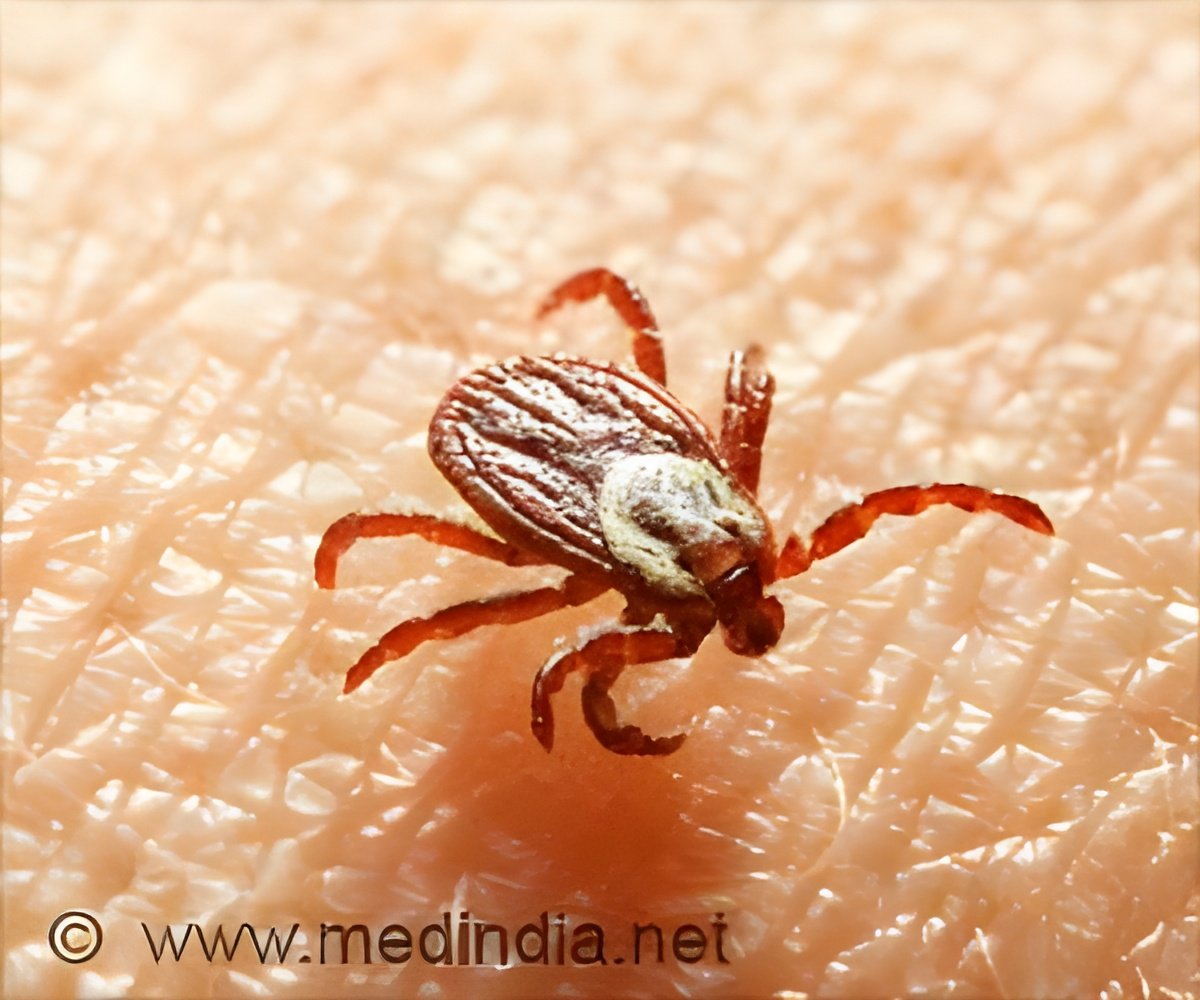
Babesiosis is a parasitic infection caused by the bite of a black-legged tick infected with Babesia microti. This disease is becoming more common in the United States, particularly in the Northeast, alongside other tick-borne illnesses such as Lyme disease (1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Babesiosis
).
Advertisement
Growing Concern Over Tick-Borne Diseases in the U.S.
In recent years, health officials and medical professionals have expressed concern over the rising cases of tick-borne diseases, particularly in regions where black-legged ticks are common. While Lyme disease remains the most prevalent, Babesiosis is becoming increasingly frequent. According to the CDC, Babesiosis has seen a significant increase, especially in the northeastern U.S.
Babesiosis is a parasitic illness caused by the Babesia microti parasite, which is transmitted through the bite of infected black-legged ticks (Ixodes scapularis). Unlike other tick-borne illnesses, such as Lyme disease, which are bacterial, Babesiosis is a parasitic infection. The parasite infects red blood cells, leading to potentially severe complications in some individuals.
Advertisement
How is Babesiosis Transmitted?
The most common way Babesiosis spreads is through the bite of an infected tick. It can also be transmitted via blood transfusions from infected donors, and, in rare cases, from an infected mother to her baby during pregnancy. However, it does not spread directly from person to person.
The severity of Babesiosis symptoms can range from mild to life-threatening. Many individuals with Babesiosis may remain asymptomatic, while others may experience the symptoms like fever and chills, Nausea, Body aches, and Fatigue.
Symptoms may appear weeks or even months after the tick bite, making it difficult to diagnose in some cases.
Advertisement
High-Risk Groups for Severe Babesiosis
While many people may clear the infection on their own, certain groups are at a higher risk of severe complications:
- Immunocompromised individuals
- Those without a spleen
- Elderly people
- Individuals with other chronic health conditions
For these groups, Babesiosis can become life-threatening, making early diagnosis and treatment crucial.
With the rise of tick-borne diseases in the U.S., particularly Babesiosis, it is essential for individuals to take precautions when spending time outdoors in areas where ticks are prevalent. Although most adults may clear the infection without treatment, those at higher risk should seek medical attention if symptoms appear.
Reference:
- Babesiosis – (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430715/)
Source-Medindia