China has just conducted the world’s first satellite-based remote surgeries, marking a revolutionary milestone in healthcare! This breakthrough could transform medical care in remote areas and combat zones.

China has successfully conducted the world’s first satellite-based, ultra-remote surgeries, a development that has the potential to revolutionize medical treatment, particularly in remote areas and high-intensity combat zones.
The groundbreaking surgeries were made possible by China’s advanced satellite technology, marking a significant step forward in the future of global healthcare.
Advertisement
How Did the Surgeries Take Place?
The surgeries were performed using the Apstar-6D satellite, which is positioned in space 36,000 km above Earth and played a key role by providing high-speed communication links between doctors and patients located far apart.
The procedures were carried out remotely, with doctors operating from three locations in China Lhasa (Tibet), Dali (Yunnan), and Sanya (Hainan) while the patients were in Beijing.
The surgeries included procedures on the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas, all of which were completed, and the patients were discharged the following day.
Advertisement
How Do Satellite Surgeries Work?
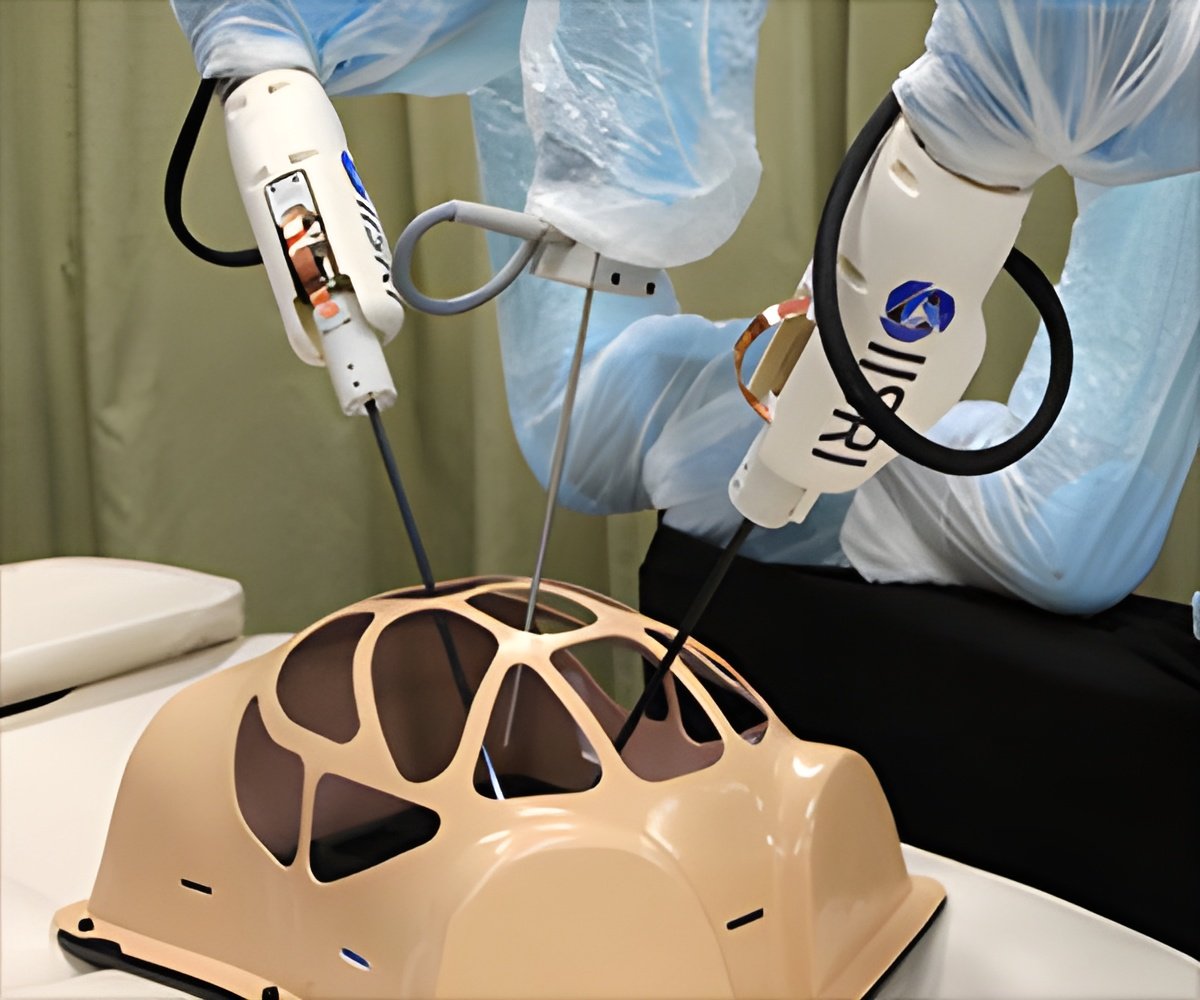
The surgical procedures were carried out using robotic surgical systems. These are highly advanced robotic tools that allow surgeons to perform precise operations remotely. The robotic arms are controlled by doctors through satellite links, and the instructions are transmitted in real-time via the Apstar-6D satellite.
One of the most remarkable aspects of this achievement was the ability to carry out a complex surgery, such as the removal of a liver tumor, remotely from Lhasa while the patient was located in Beijing.
To ensure success, the data was carefully optimized to reduce communication delays, also known as latency. The satellite’s high-speed data transmission and advanced traffic management systems allowed the surgeons to perform the surgery with minimal delay, close to the physical limits of satellite communication.
Advertisement
The Role of the Apstar-6D Satellite
The Apstar-6D satellite, launched in 2020, is the centerpiece of this achievement. It is designed to provide fast, reliable broadband internet and communication services.
This satellite can transmit data at speeds of up to 50 gigabits per second, which is critical for real-time remote surgery. With a lifespan of 15 years, the Apstar-6D is part of a planned constellation of up to four satellites that will help connect remote areas, aircraft, and ships, offering seamless broadband service.
These satellites are designed to address communication gaps and provide high-speed internet and data exchange for areas that typically have limited access to modern communication networks.
A major challenge in many parts of the world, especially in rural or conflict-prone areas, is the lack of access to quality healthcare. By using satellite technology, China has demonstrated that medical care can be extended to the most remote areas.
This provides faster and more efficient medical responses but could also make surgeries possible in situations where they were once thought to be impossible, such as in combat zones or disaster-stricken regions.
China’s achievements in this field not only highlight the potential for future medical breakthroughs but also show the significant effect that advanced technologies, like satellite communications and robotic surgery, can have on improving health outcomes across the globe.
Reference:
- Surgery via satellite: China conducts ultra-remote medical procedures in world first- (https:www.scmp.com/news/china/science/article/3293260/surgery-satellite-china-conducts-ultra-remote-medical-procedures-world-first)
Source-Medindia