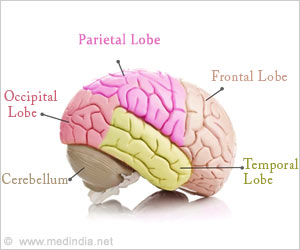
It is the point of origin of visual difficulties in many diseases such as dyslexia and glaucoma.
Decoding Hidden Territory
The area contains two tiny major compartments that are located very deep inside the brain. This made it difficult to be assessed so far, thereby adding to the struggle to decode visual sensory processing.
However, the study team used unique neuroimaging data with high spatial resolution on a specialized magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machine at the MPI-CBS in Leipzig to explore the area.
It was found that the two major compartments of the visual sensory thalamus are characterized by different amounts of brain white matter (myelin), as detected in novel MRI data, obtained from post-mortem studies of developmental dyslexia.
“The finding that we can display visual sensory thalamus compartments in living humans is fantastic, as it will be a great tool for understanding visual sensory processing both in health and disease in the near future”, says first author Christa Mller-Axt.
Source: Medindia