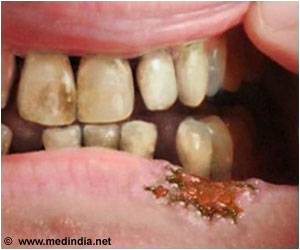
Each individual’s status was defined as positive/negative for oral cancer/OPMDs and histologic confirmation of epithelial dysplasia (ED) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) was performed for positive status.
Follow-up status of those that screened negative was monitored via state-linked electronic health records. Information on demography, habitual, lifestyle and familial risk factors was obtained, and expired carbon monoxide levels (in ppm) were assessed using a monitor.
A Deep-Learning Method for Oral Cancer Diagnosis
Input features (n=40) and histologic diagnoses were used to populate 12 machine learning algorithms with 80:20 train-test splitting applied to the data randomly during development.
Advertisement
Recursive feature elimination with 10-fold cross-validation was used for feature selection while synthetic-minority-oversampling-technique with edited-nearest-neighbors was implemented for class imbalance correction.
Internal validation was conducted with the unused 20% data with the comparison of outputs using McNemar’s test used for optimal model selection Performance metrics included recall, specificity, and F1-score.
Source: Eurekalert