-
Mercury, a known environmental toxin, raises concerns about its role in neurological damage and neurodegenerative diseases - Genchi et al and Bjørklund et al, explore the complex mechanisms through which mercury induces neurotoxicity
- Despite global exposure through activities like coal combustion and industrial processes, further research is needed to mitigate the potential impact of mercury on neuronal health
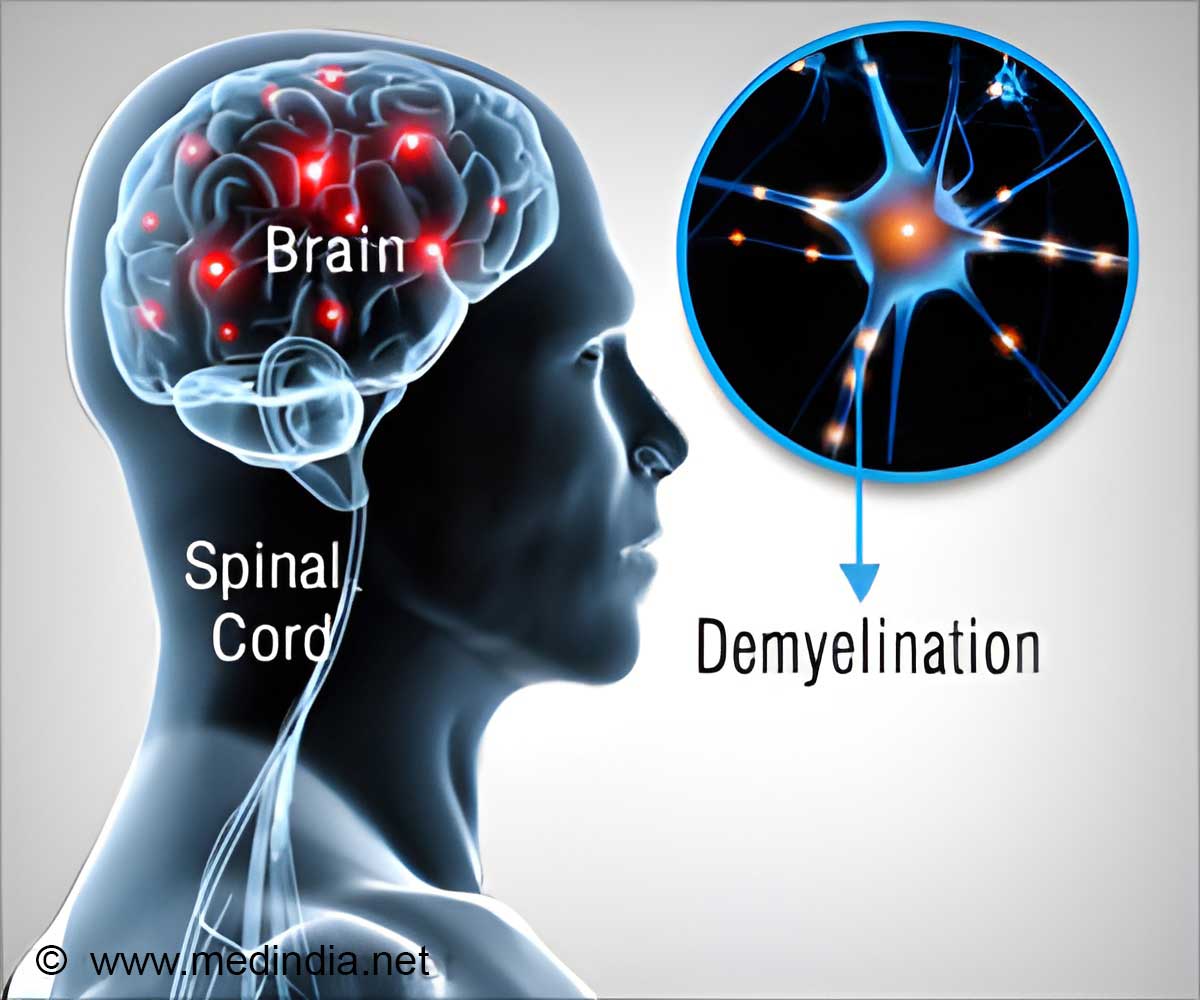
Mercury, a heavy metal, is a well-known environmental toxin that poses a threat to human health. Its ability to accumulate in the body, including the central nervous system, has raised concerns about its potential involvement in neurological damage and neurodegenerative diseases.
Advertisement
Mercury Exposure and Neurotoxicity
Several studies have investigated the neurotoxic effects of mercury exposure, with a particular focus on its impact on neuronal function and structure. Genchi et al highlighted the mechanisms through which mercury induces neurotoxicity. They emphasize that mercury can cross the blood-brain barrier and accumulate in the brain, where it interacts with cellular components, disrupting crucial neuronal processes.
Mercury exists in various forms, including elemental mercury, inorganic mercury compounds, and organic mercury compounds like methylmercury. Each form has distinct properties and mechanisms of toxicity.
The link between mercury exposure and the development or exacerbation of neurodegenerative diseases has gained attention in recent research. The study published by Bjørklund et al, examines the potential association between mercury exposure and neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimers disease and Parkinsons disease.
Bjørklund et al. present evidence suggesting that mercury may contribute to the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases through various mechanisms, including the formation of neurotoxic protein aggregates, oxidative stress, and disruption of metal homeostasis. There prevails the need for further research to elucidate the intricate interactions between mercury and molecular pathways implicated in neurodegeneration.
Advertisement
Link Between Neurodegenerative Diseases and Mercury Exposure
The molecular mechanisms underlying mercury-induced neurotoxicity are complex and multifaceted.
Methylmercury and Brain Accumulation:
Methylmercury, an organic form of mercury, is known for its ability to accumulate in the central nervous system. This form of mercury is particularly relevant concerning neurodegenerative diseases (1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Mercury Involvement in Neuronal Damage and in Neurodegenerative Diseases
).
Oxidative Stress and Neurotoxicity:
Mercury exposure has been linked to oxidative stress, a condition where there is an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body’s ability to detoxify them. Oxidative stress is a common feature in neurodegenerative diseases, and mercury-induced oxidative stress may contribute to neuronal damage.
Inflammation and Immune Response:
Mercury exposure has been shown to induce inflammation and affect the immune response in the central nervous system. Chronic inflammation is implicated in the progression of neurodegenerative diseases, and mercury’s inflammatory effects may contribute to the development or exacerbation of these conditions.
Protein Misfolding and Aggregation:
Mercury has been suggested to play a role in the misfolding and aggregation of proteins, a common characteristic of several neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
Advertisement
Widespread Mercury Exposure
-
Mercury is a global pollutant that can travel long distances through the atmosphere. Even countries that do not have significant local sources of mercury may experience exposure due to the global transport of mercury emissions. - Significant industrial activities, including those involving coal combustion, metal processing, and mining, may experience elevated levels of mercury emissions.
- Coal-burning power plants are a major source of mercury emissions.
- Mercury bioaccumulates in aquatic ecosystems, leading to higher concentrations in certain fish species.
While the existing evidence suggests a connection between mercury exposure and neurodegenerative diseases, further research is essential to unravel the specific mechanisms and establish causation. This knowledge is crucial for developing preventive strategies and therapeutic interventions to mitigate the impact of mercury on neuronal health.
Awareness and regulatory measures are imperative to reduce human exposure and protect vulnerable populations from the potential neurotoxic effects of mercury.
Reference:
- Mercury Involvement in Neuronal Damage and in Neurodegenerative Diseases – (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29777524/)
Source-Medindia