Powassan virus infections are most commonly recorded in areas of Russia, the northeastern United States, and the Great Lakes region of the United States and Canada. Predominantly reported cases have emerged in states such as Massachusetts, Minnesota, Wisconsin, New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, and Maine.
. In essence, from the moment an infected tick bites, it generally takes one to four weeks for symptoms to manifest.
Symptoms and Signs:
-
Fever - Headache
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Altered mental state or confusion
- Seizures
- Speech difficulties
- Paralysis
Ordinarily, initial symptoms like fever and headache may precede more severe manifestations such as confusion or seizures.
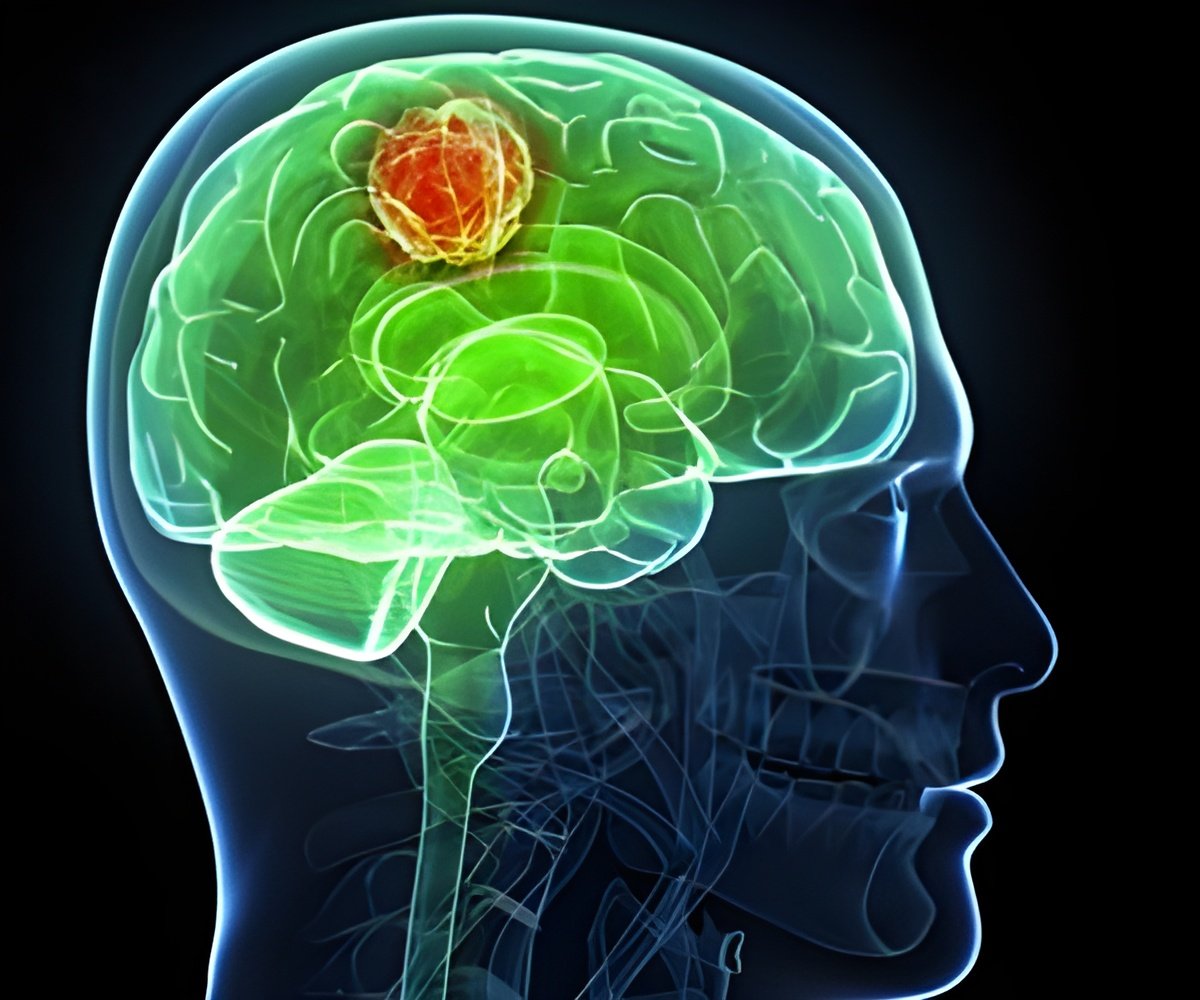
Powassan virus has the potential to infiltrate the brain subsequent to a tick bite. This invasion can lead to encephalitis, characterized by brain inflammation. Even individuals who recover from the illness might suffer long-term consequences arising from encephalitis.
Mode of Transmission of Powassan Virus Disease
Powassan virus is a type of flavivirus, an RNA virus commonly transmitted through mosquitoes and ticks, the causative agent behind Powassan virus infections. Other examples of flaviviruses include the viruses responsible for dengue fever https://www.medindia.net/patients/lifestyleandwellness/top-15-dos-and-donts-for-preventing-and-managing-dengue-fever.htm Top 15 Dos and Don’ts for Preventing and Managing Dengue Fever, West Nile virus, and Zika virus.
Transmission of Powassan virus occurs via the bite of an infected Ixodes tick. Ixodes scapularis, also known as black legged or deer ticks, are the primary vectors for human transmission. Although Ixodes cookei (groundhog tick) and Ixodes marxi (squirrel tick) can also harbor the virus, they seldom bite humans. Notably, unlike certain other tick-borne illnesses, Powassan virus transmission can occur within a few minutes of tick attachment.
Diagnosis of Powassan Virus
Diagnosis of Powassan virus disease may involve the following examinations:
- Blood tests
- Lumbar puncture or spinal tap
- Imaging techniques like CT scans or MRI, especially if neurological symptoms are present
Treatment and Management of Powassan Virus
No antiviral medications specifically target Powassan virus infections. Hospitalization is advised for encephalitis cases. For milder symptoms, individuals can consult healthcare professionals about symptom management at home, including rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications.
In severe cases, hospital-based treatment may involve:
- Anti Seizure medications
- Oxygen supplementation or mechanical ventilation
- Intravenous fluids to maintain hydration
- Corticosteroids to mitigate inflammation
- Tube feeding in cases of self-feeding inability
Mild Powassan virus cases have not led to known fatalities.
Approximately 10% of individuals afflicted with brain or spinal cord infections stemming from Powassan virus succumb to the disease.
Even post-recovery, about half of those who experienced severe symptoms, including Powassan virus encephalitis, may grapple with enduring health problems such as facial paralysis (hemiplegia), memory impairment, weakness, and muscle loss.
Prevention of Powassan Virus
Mitigating the risk of Powassan virus entails evading tick bites. Precautionary measures include:
-
Keeping grass below 5 inches in height - Staying on clear pathways when traversing wooded areas
- Applying tick-repellent bug sprays containing DEET or other proven ingredients
- Donning clothing that covers skin extensively when in grassy or wooded regions
- Thoroughly inspect the entire body for ticks after outdoor exposure, with particular
- Seeking advice from veterinarians to shield pets from ticks and checking pets for ticks regularly
attention to the groin, armpits, neck, and head; assistance might be needed for hard-to-see areas
Note: Contact your Doctor immediately if the following symptoms arises:
-
Cognitive impairment or other mental shifts - Seizures
- Speech difficulties
- Paralysis
Reference :
- Powassan Virus – (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/25092-powassan-virus)
Source: Medindia