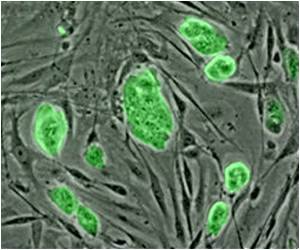
The researchers designed co-culture systems in vitro and co-implantation systems in vivo. Based on these systems, they found that breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs) inhibit their own capacity through the BSCS-derived secretome. By means of screening, bioluminescent imaging and others, they also found that DKK1 plays a pivotal role in the secretome. DKK1 was identified as a pivotal molecule that autonomously diminishes the CSC population and subsequently promotes breast cancer metastatic colonization.
Further experiments showed that this autonomous restraint of BCSCs can prompt disseminated tumor cells (DTCs), which remain largely dormant after arriving at distant sites, to exit from dormancy and then achieve metastatic colonization. A small-molecule inhibitor of the DKK1, however, can achieve a nearly complete blockade of lung metastasis in many BCSC metastasis models.
Ferroptosis, a non-apoptotic cell death process, is caused by abnormal metabolism and lipid peroxidation. Compared with those in primary mammary cancers, cancer cells from lung metastases are under higher oxidative and ferroptotic stress. The researchers revealed that the highly invasive CSCs have a relatively high concentration in lung metastases, where CSCs can secrete DKK1 that restrain CSCs. As CSCs are highly sensitive to ferroptosis, CSC-secreted DKK1 protects cells in lung metastases from ferroptosis and thus contributes to metastatic outgrowth.
The findings of this study reveal the role of CSC-regulated phenotypic plasticity in metastatic colonization, and provide new therapeutic approaches to effectively inhibit metastases.
Source: Eurekalert